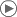Vaihtoehtoiset kirjoitusmuodot
- (vanhentunut) republick
- (vanhentunut) republique
Määritelmät
Substantiivi
- A state where sovereignty rests with the people or their representatives, rather than with a monarch or emperor; a country with no monarchy.
- (archaic) A state, which may or may not be a monarchy, in which the executive and legislative branches of government are separate.
- One of the subdivisions constituting Russia. See oblast.
- One of the subdivisions that made up the former Yugoslavia.
Esimerkit
- The United States is a republic; the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is a constitutional monarchy.
- “[…] We are engaged in a great work, a treatise on our river fortifications, perhaps ? But since when did army officers afford the luxury of amanuenses in this simple republic ?[...]”
- Republicanism is the political principle of the separation of the executive power (the administration) from the legislative; despotism is that of the autonomous execution by the state of laws which it has itself decreed.[...]Therefore, we can say: the smaller the personnel of the government (the smaller the number of rulers), the greater is their representation and the more nearly the constitution approaches to the possibility of republicanism; thus the constitution may be expected by gradual reform finally to raise itself to republicanism. None of the ancient so-called "republics" knew this system, and they all finally and inevitably degenerated into despotism under the sovereignty of one, which is the most bearable of all forms of despotism.
- The Republic of Udmurtia is west of the Permian Oblast.
Taivutusmuodot
| Monikko | republics |
A state where sovereignty rests with the people or their representatives, rather than with a monarch or emperor; a country with no monarchy.

World's states colored by systems of government: Parliamentary systems: Head of government is elected or nominated by and accountable to the legislature. Constitutional monarchy with a ceremonial monarch Parliamentary republic with a ceremonial president Parliamentary republic with an executive president Presidential system: Head of government (president) is popularly elected and independent of the legislature. Presidential republic Hybrid systems: Semi-presidential republic: Executive president is independent of the legislature; head of government is appointed by the president and is accountable to the legislature. Assembly-independent republic: Head of government (president or directory) is elected by the legislature, but is not accountable to it. Other systems: Theocratic republic: Supreme Leader is both head of state and faith and holds significant executive and legislative power Semi-constitutional monarchy: Monarch holds significant executive or legislative power. Absolute monarchy: Monarch has unlimited power. One-party state: Power is constitutionally linked to a single political party. Military junta: Committee of military leaders controls the government; constitutional provisions are suspended. Governments with no constitutional basis: No constitutionally defined basis to current regime, i.e., provisional governments or Islamic theocracies. Dependent territories or places without governments Note: this chart represents the de jure systems of government, not the de facto degree of democracy.
A state where sovereignty rests with the people or their representatives, rather than with a monarch or emperor; a country with no monarchy.

The Swiss cantons displayed on the cupola of the Federal Palace