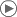| Kieli | Käännökset |
|---|---|
| espanja | linfa |
| hollanti | lymfe |
| italia | lympha, linfa |
| japani | リンパ液 (rinpa-eki), 淋巴, リンパ (rinpa) |
| kreikka | λύμφη (lýmfi), λέμφος (lémfos) |
| norja | lymfe |
| portugali | linfa |
| puola | limfa |
| ranska | lymphe |
| ruotsi | lymfa, lymfsystemet |
| saksa | Lymphe |
| suomi | imuneste, lymfa |
| tanska | lymfe |
| tšekki | míza, lymfa |
| venäjä | лимфа (limfa) |
Määritelmät
Substantiivi
- (obsolete, literary) Pure water.
- (archaic, botany) The sap of plants.
- (physiology) A colourless, watery, coagulable bodily fluid which bathes the tissues and is carried by the lymphatic system into the bloodstream; it resembles blood plasma in containing white blood cells and especially lymphocytes but normally few red blood cells and no platelets.
- (immunology) The discharge from a sore, inflammation etc.
Esimerkit
- She lay face-down, an infected puncture point on the inside of her thigh oozing a faint lymph.
Taivutusmuodot
| Monikko | lymphs |
Luokat
(physiology) A colourless, watery, coagulable bodily fluid which bathes the tissues and is carried by the lymphatic system into the bloodstream; it resembles blood plasma in containing white blood cells and especially lymphocytes but normally few red blood cells and no platelets.

Human lymph, obtained after a thoracic duct injury
(physiology) A colourless, watery, coagulable bodily fluid which bathes the tissues and is carried by the lymphatic system into the bloodstream; it resembles blood plasma in containing white blood cells and especially lymphocytes but normally few red blood cells and no platelets.

Diagram showing the formation of lymph from interstitial fluid (labeled here as "Tissue fluid"). Note how the tissue fluid is entering the blind ends of lymph capillaries (shown as deep green arrows).
(physiology) A colourless, watery, coagulable bodily fluid which bathes the tissues and is carried by the lymphatic system into the bloodstream; it resembles blood plasma in containing white blood cells and especially lymphocytes but normally few red blood cells and no platelets.

Formation of interstitial fluid from blood. Starling forces are labelled: the hydrostatic pressure is higher proximally, driving fluid out; oncotic forces are higher distally, pulling fluid in.