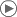Synonyymit
| Kieli | Käännökset |
|---|---|
| espanja | eigenvector, autovector, vector propio |
| hollanti | eigenvector |
| italia | autovettore |
| japani | 固有ベクトル (koyū bekutoru) |
| kreikka | ιδιοδιάνυσμα (idiodiánysma) |
| portugali | autovetor, vetor próprio |
| puola | wektor własny |
| ranska | vecteur propre |
| ruotsi | egenvektor |
| saksa | Eigenvektor |
| suomi | ominaisvektori |
| tanska | egenvektor |
| venäjä | собственный вектор (sobstvennyi vektor) |
| viro | omavektor |
Määritelmät
Substantiivi
- (linear algebra) A vector that is only scaled (not rotated out of its span) under a particular linear transformation; a left or right eigenvector depending on context; (more formally) given a linear transformation A, a vector x such that Ax=λx [or xA=λx] for some scalar λ (called the eigenvalue).
- (physics, engineering) A right eigenvector; given a matrix A, the eigenvector of the transformation "left-side multiplication by A."
Taivutusmuodot
| Monikko | eigenvectors |
(linear algebra) A vector that is only scaled (not rotated out of its span) under a particular linear transformation; a left or right eigenvector depending on context; (more formally) given a linear transformation A, a vector x such that Ax=λx [or xA=λx] for some scalar λ (called the eigenvalue).

In this shear mapping the red arrow changes direction, but the blue arrow does not. The blue arrow is an eigenvector of this shear mapping because it does not change direction, and since its length is unchanged, its eigenvalue is 1.
(linear algebra) A vector that is only scaled (not rotated out of its span) under a particular linear transformation; a left or right eigenvector depending on context; (more formally) given a linear transformation A, a vector x such that Ax=λx [or xA=λx] for some scalar λ (called the eigenvalue).
A 2 × 2 real and symmetric matrix representing a stretching and shearing of the plane. The eigenvectors of the matrix (red lines) are the two special directions such that every point on them will just slide on them.
(linear algebra) A vector that is only scaled (not rotated out of its span) under a particular linear transformation; a left or right eigenvector depending on context; (more formally) given a linear transformation A, a vector x such that Ax=λx [or xA=λx] for some scalar λ (called the eigenvalue).
Matrix A acts by stretching the vector x, not changing its direction, so x is an eigenvector of A.