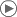Synonyymit
Määritelmät
Substantiivi
- (biochemistry) A white crystalline organic compound, C₆H₈O₆, found in citrus fruits and many vegetables; it is an antioxidant and an efficient scavenger of free radicals.
Luokat
(biochemistry) A white crystalline organic compound, C₆H₈O₆, found in citrus fruits and many vegetables; it is an antioxidant and an efficient scavenger of free radicals.
L-ascorbic acid
(biochemistry) A white crystalline organic compound, C₆H₈O₆, found in citrus fruits and many vegetables; it is an antioxidant and an efficient scavenger of free radicals.

Ball-and-stick model of the L-ascorbic acid (vitamin C) molecule, C6H8O6, as found in the crystal structure. X-ray diffraction data from J. Mol. Struct.: THEOCHEM (1997) 419, 139-154. Model constructed in CrystalMaker 8.1. Image generated in Accelrys DS Visualizer.
(biochemistry) A white crystalline organic compound, C₆H₈O₆, found in citrus fruits and many vegetables; it is an antioxidant and an efficient scavenger of free radicals.

Canonical forms in resonance