Ääntäminen
 Southern England
Southern England- Tuntematon aksentti:
- IPA: /ˈfeɪɡəsaɪt/
| Kieli | Käännökset |
|---|---|
| hollanti | fagocyt |
| italia | fagocitare, fagocita, fagocito |
| portugali | fagócito |
| ranska | engloutir, phagocyte |
| ruotsi | fagocyt, ätarcell |
| saksa | Phagozyt |
| suomi | fagosyytti, syöjäsolu, fagosytoida |
| tšekki | fagocyt |
| venäjä | фагоцит (fagotsit / fagocit) |
Määritelmät
Substantiivi
- (cytology) A cell of the immune system, such as a neutrophil, macrophage or dendritic cell, that engulfs and destroys viruses, bacteria and waste materials, or in the case of mature dendritic cells; displays antigens from invading pathogens to cells of the lymphoid lineage.
Verbi
- (transitive) To phagocytize
Taivutusmuodot
| Partisiipin perfekti | phagocyted |
| Imperfekti | phagocyted |
| Partisiipin preesens | phagocyting |
| Monikko | phagocytes |
| Yksikön kolmannen persoonan indikatiivin preesens | phagocytes |
(cytology) A cell of the immune system, such as a neutrophil, macrophage or dendritic cell, that engulfs and destroys viruses, bacteria and waste materials, or in the case of mature dendritic cells; displays antigens from invading pathogens to cells of the lymphoid lineage.

Scanning electron micrograph of a neutrophil phagocytosing anthrax bacilli (orange)
(cytology) A cell of the immune system, such as a neutrophil, macrophage or dendritic cell, that engulfs and destroys viruses, bacteria and waste materials, or in the case of mature dendritic cells; displays antigens from invading pathogens to cells of the lymphoid lineage.

Phagocytosis in three steps: 1. Unbound phagocyte surface receptors do not trigger phagocytosis. 2. Binding of receptors causes them to cluster. 3. Phagocytosis is triggered and the particle is taken up by the phagocyte.
(cytology) A cell of the immune system, such as a neutrophil, macrophage or dendritic cell, that engulfs and destroys viruses, bacteria and waste materials, or in the case of mature dendritic cells; displays antigens from invading pathogens to cells of the lymphoid lineage.
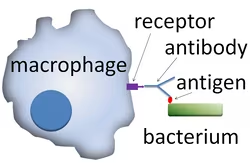
Macrophages have special receptors that enhance phagocytosis (not to scale)