Ääntäminen
 Southern England
Southern England- Tuntematon aksentti:
- IPA: /juːˈd͡ʒɛnɪks/
Määritelmät
Substantiivi
- (sociology, biology) A social philosophy or practice which advocates the improvement of human hereditary qualities through selective breeding, either by encouraging people with superior genetic qualities to reproduce (positive eugenics), or discouraging people with inferior genetic qualities from reproducing (negative eugenics), or by technological means.
(sociology, biology) A social philosophy or practice which advocates the improvement of human hereditary qualities through selective breeding, either by encouraging people with superior genetic qualities to reproduce (positive eugenics), or discouraging people with inferior genetic qualities from reproducing (negative eugenics), or by technological means.

A 1930s exhibit by the Eugenics Society. Some of the signs read "Healthy and Unhealthy Families", "Heredity as the Basis of Efficiency", and "Marry Wisely".
(sociology, biology) A social philosophy or practice which advocates the improvement of human hereditary qualities through selective breeding, either by encouraging people with superior genetic qualities to reproduce (positive eugenics), or discouraging people with inferior genetic qualities from reproducing (negative eugenics), or by technological means.
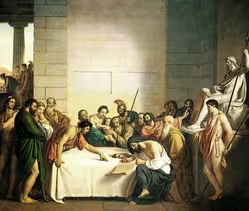
Giuseppe Diotti's The selection of the infant Spartans (1840)
(sociology, biology) A social philosophy or practice which advocates the improvement of human hereditary qualities through selective breeding, either by encouraging people with superior genetic qualities to reproduce (positive eugenics), or discouraging people with inferior genetic qualities from reproducing (negative eugenics), or by technological means.

Marie Stopes in her laboratory, 1904